Introduction
The minimum wage in the United States has been a subject of debate for years, with many advocating for higher wages to combat the rising cost of living. As we move into 2025, several states have implemented new minimum wage laws, increasing hourly rates across the country. This article provides a comprehensive state-by-state breakdown of the new minimum wages, discusses the economic impact, and highlights the pros and cons of wage hikes.
Federal Minimum Wage Update for 2025
As of 2025, the federal minimum wage remains at $7.25 per hour, a rate that has been unchanged since 2009. However, some lawmakers continue to push for an increase, with proposals suggesting a gradual rise to $15 per hour over the coming years.
The Biden administration and labor advocates emphasize that inflation and increased living costs necessitate a federal wage increase. However, opposition from businesses and some legislators has stalled progress at the national level, leading to state-by-state wage reforms instead.
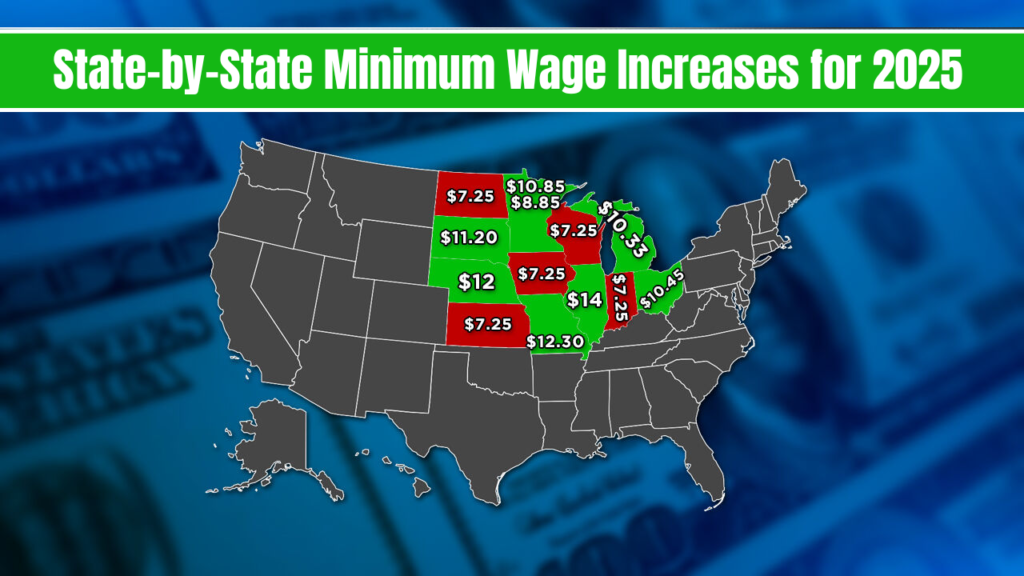
State-by-State Minimum Wage Increases for 2025
Many states have taken independent action to raise their minimum wage beyond the federal level. Below is an overview of notable state minimum wage increases effective in 2025:
States Increasing Minimum Wage in 2025
States Raising Minimum Wage to $15 or More
- California: $16.50 (for businesses with 26+ employees)
- New York: $16.00 (New York City, Westchester, Long Island); $15.00 (Rest of the state)
- Washington: $15.74 (indexed to inflation)
- Massachusetts: $15.50
- Oregon: $15.00 (Portland metro), $14.20 (standard rate), $13.20 (rural areas)
States with Moderate Wage Increases ($12-$15 Range)
- Colorado: $14.50
- Arizona: $14.35
- Maine: $14.15
- Vermont: $13.89
States with Smaller Wage Adjustments ($10-$12 Range)
- Montana: $11.40
- South Dakota: $11.25
- Ohio: $10.75
- Missouri: $12.30
States That Have Not Raised Wages Beyond Federal Minimum
Several states continue to follow the federal minimum wage of $7.25 per hour, including:
- Texas
- Alabama
- Louisiana
- Mississippi
- South Carolina
Economic Impact of Minimum Wage Increases
The decision to raise minimum wages has wide-reaching economic consequences, both positive and negative. Below, we explore the potential impacts:
Benefits of Raising the Minimum Wage
- Higher Earnings for Low-Income Workers
- Wage increases help lift millions of workers out of poverty.
- Boost to Local Economies
- More disposable income leads to higher consumer spending.
- Improved Employee Retention
- Reducing turnover saves businesses training and hiring costs.
Challenges of Increasing the Minimum Wage
- Potential Job Losses
- Small businesses may struggle with higher payroll expenses.
- Price Increases
- Companies may pass labor costs onto consumers via higher prices.
- Automation and Reduced Hiring
- Businesses may invest in technology to replace human workers.

How Employers Are Responding to Wage Hikes
Adjustments in Business Strategies
- Some businesses increase prices to offset higher wages.
- Larger corporations may reduce workforce hours.
- Small businesses seek tax incentives or government aid to balance wage hikes.
Worker Productivity & Training
- Employers are focusing on worker efficiency.
- Companies are investing in training programs to justify higher wages.
Conclusion
The minimum wage increase in 2025 represents a significant shift in the labor market, with more states raising wages despite federal stagnation at $7.25 per hour. While higher wages improve worker livelihoods and economic growth, concerns about job losses, inflation, and automation persist. Moving forward, continued discussions at the federal and state levels will shape wage policies for years to come.
FAQs
1. What is the federal minimum wage in 2025?
The federal minimum wage remains at $7.25 per hour, unchanged since 2009.
2. Which states have the highest minimum wage in 2025?
California, Washington, and New York lead with wages above $15 per hour.
3. How does raising the minimum wage impact small businesses?
Small businesses may face higher labor costs, leading to potential price increases, job cuts, or reduced hiring.
4. Why hasn’t the federal minimum wage increased since 2009?
Political debates and opposition from business groups have stalled federal wage hikes, leaving states to decide their own increases.
5. What are the long-term effects of minimum wage hikes?
Long-term effects include higher worker earnings, possible job losses, increased automation, and rising consumer prices.



